DECAF UNPACKED:
THE BEAN WITHOUT THE BUZZ
THE BEAN WITHOUT THE BUZZ
FREQUENT ASKED QUESTIONS
1. What Is Decaffeinated Coffee?
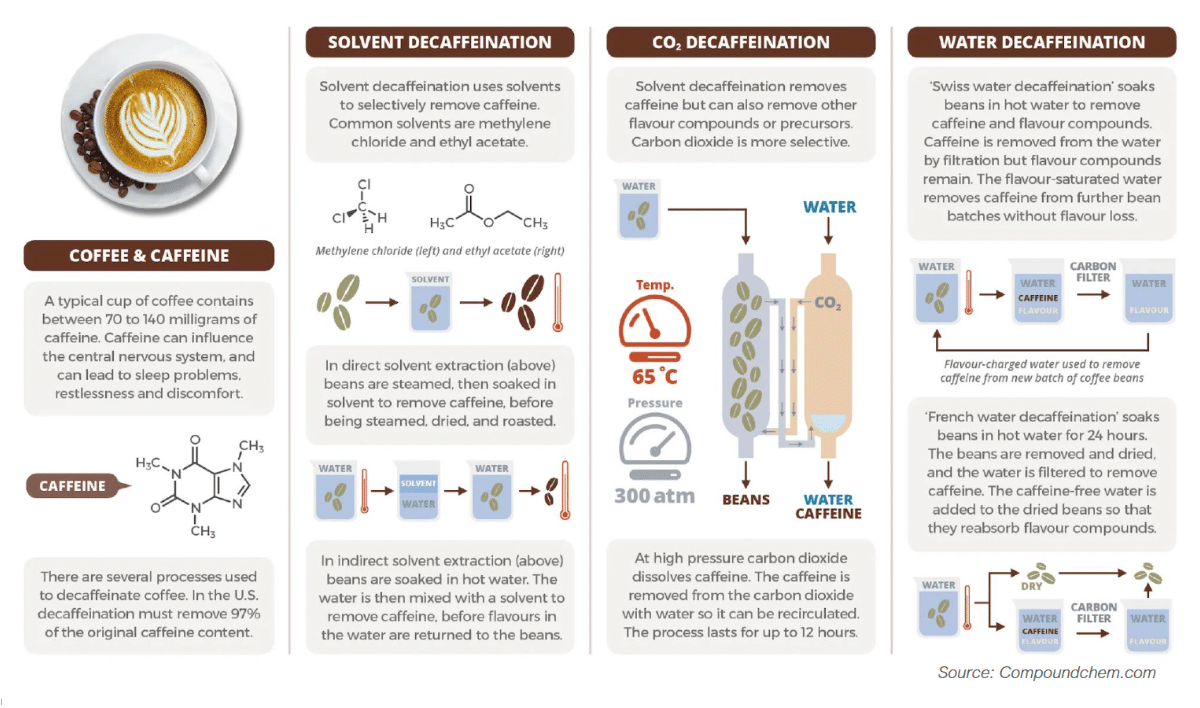
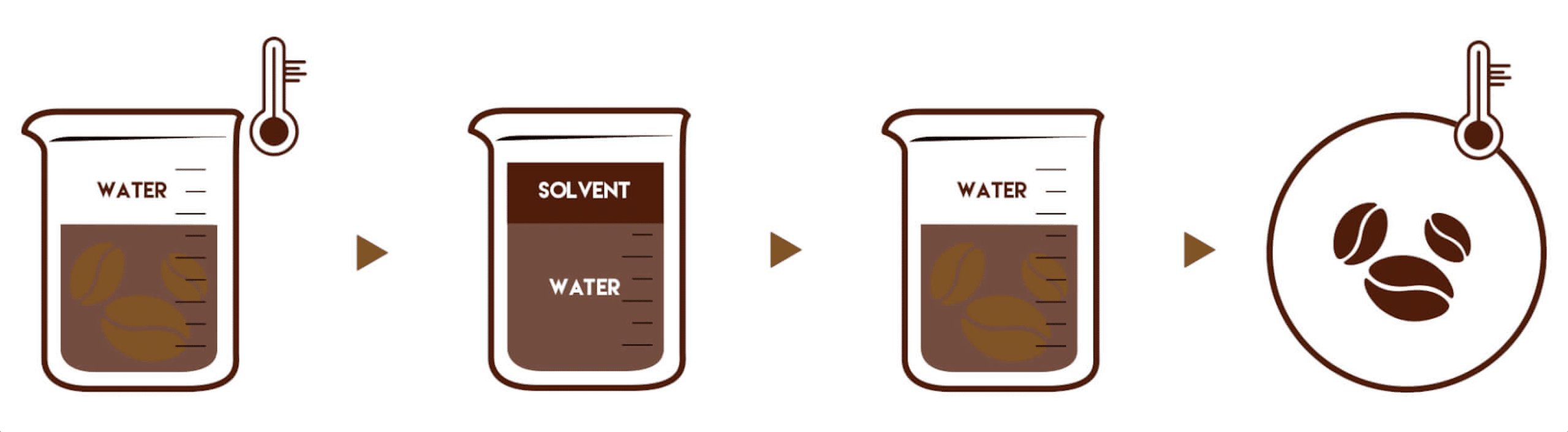
Decaffeinated coffee is made from the same beans as regular coffee, with the caffeine removed from the raw beans before roasting. While often referred to as ‘caffeine-free,’ decaf coffee still contains a small amount of caffeine -typically up to 0.1%. There are several methods for caffeine removal, but we focus on natural processes that aim to retain as much of the coffee’s original flavour and aroma as possible.
2. Is Decaffeinated Coffee Completely Caffeine-Free?
Although many people refer to decaffeinated coffee as ‘caffeine-free’, this is not entirely accurate. According to EU regulations, decaffeinated coffee can contain up to 0.1% caffeine. For comparison, you would have to drink about 10 cups of decaf to match the caffeine content of just one regular cup.
Here’s a quick breakdown of caffeine content in different types of coffee beans:
- Decaffeinated coffee: 0.1% caffeine
- so called ‘Low-caffeine’ coffee:
- Laurina : 0.2 – 0.3% caffeine
- Aramosa: 0.7 – 0.8% caffeine
- Arabica coffee: 1.2 – 1.7% caffeine
- Robusta coffee: up to 2.7% caffeine
The roasting process has minimal effect on caffeine content, but the brewing method can influence how much caffeine ends up in your cup. For instance, an espresso (60ml) typically has less caffeine than a regular cup of filter coffee (90ml), even though espresso has a stronger flavour.
3. How Much Decaffeinated Coffee Can You Drink Per Day?
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) recommends that healthy adults consume no more than 400mg* of caffeine per day. However, individuals with certain health conditions, such as those with heart disease or pregnant women, should limit their caffeine intake.
To calculate your personal caffeine tolerance, a general guideline is 3mg of caffeine per kilogram of body weight. For example, a 70kg person can safely consume up to 210mg of caffeine per day.
Here’s how caffeine in decaf compares to other drinks:
-
Decaffeinated coffee (200ml): 3-7mg of caffeine
-
Filter coffee (200ml): 90mg of caffeine
-
Espresso (60ml): 80mg of caffeine
Keep in mind that caffeine takes around 8-12 hours to be processed by the body, so it’s best to avoid large doses at once. Other foods and drinks, such as tea, energy drinks, and chocolate, also contain caffeine, so remember to factor those into your daily intake.
Up to 400 milligrams (mg) of caffeine a day appears to be safe for most healthy adults. That’s roughly the amount of caffeine in 4 cups of brewed coffee, 10 cans of cola or 2 ‘energy shot’ drinks. Keep in mind that the actual caffeine content in beverages varies widely, especially among energy drinks.
NOTES, CREDITS, REFERENCES
NOTES from Our Quality Lab Team
1. The Bigger Picture
Overall, it’s important to keep in mind that coffee contains over 400 natural compounds, with caffeine being one of them. When considering decaffeination, it’s crucial to understand that removing caffeine is just one part of the process, as all these compounds work together to shape the flavour and aroma of the brewed beverage.
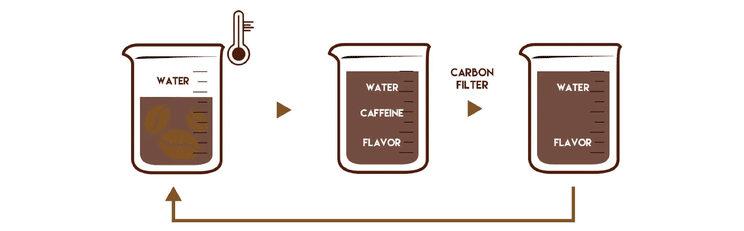
2. Update on Dichloromethane (DCM) in Decaffeinated Coffee
In a recent meeting with the European Coffee Federation, we received an update on the EU’s ongoing review of Dichloromethane (DCM), a solvent sometimes used in the decaffeination process.
European authorities are currently reassessing DCM to ensure that safety standards continue to reflect the latest scientific understanding. As part of this, DCM is being reclassified to better reflect potential long-term risks at high exposure levels — though it’s important to emphasize that this does not mean products on the market today are unsafe.
Decaffeinated coffee already follows strict regulations, and the trace amounts of DCM allowed are well below levels that could pose any risk to consumers. The current review is simply aimed at refining these limits to provide even more clarity and assurance.
The key takeaway:
There is no immediate risk to consumers. Decaffeinated coffee remains safe, and any future updates to regulations will be made to further strengthen consumer protection and maintain high safety standards across the industry.
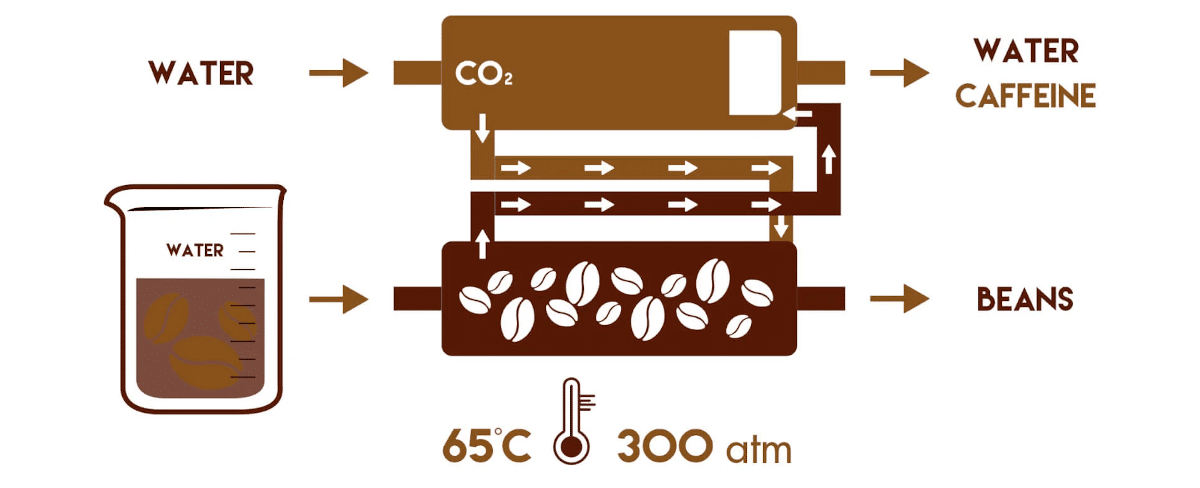
*CR3 invented the liquid carbon dixoxide method (or subcritical method) in the 80´s. This was a further development of the supercrital method by Kurt Zosel. CR3´s method is using less pressure and lower temperatures, but CO₂ needs to be evaporated and liquified during the process.
ZHAW Coffee Excellence Center
Sciencing – How To Extract Pure Caffeine From Coffee
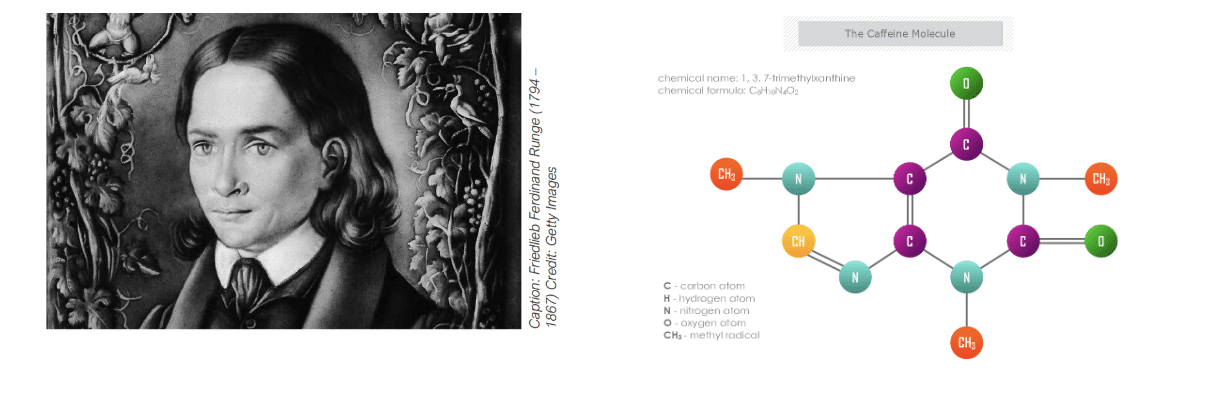
New Scientist – Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge, the godfather of caffeine
A big thank you to Ivan from Seabridge’s Quality Lab and Celest from our Antwerp HQ Quality Lab for sharing your valuable expertise!
A big thank you to Ivan from Seabridge Lab and Celest from our Antwerp HQ Lab for sharing your valuable expertise!