FROM TREE TO CUP
UNDERSTANDING COFFEE’S CARBON FOOTPRINT
UNDERSTANDING COFFEE’S CARBON FOOTPRINT
NOTES, CREDITS, REFERENCES
*interpretation graphics Quantis LCA (2023)
European market adaptation Life Cycle Asessment (LCA) of a lungo cup of coffee made from a Nespresso original capsule compared with other coffee systems in Europe
Carbon Footprint of the Nespresso Original System
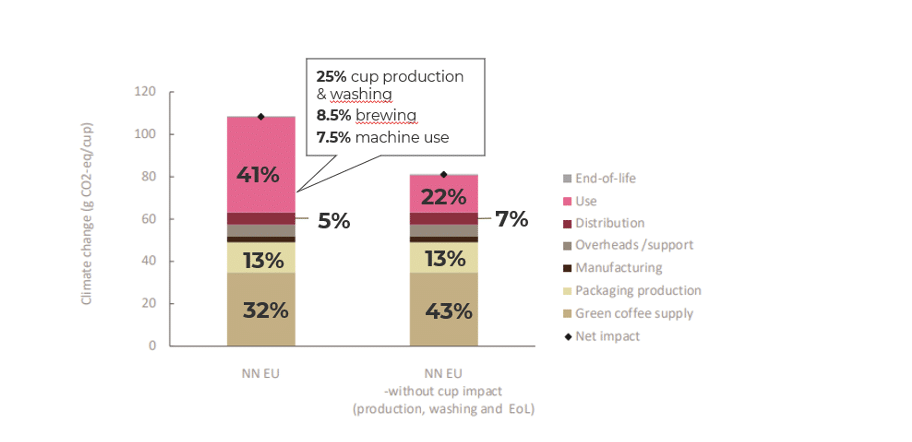
A 110 ml cup of Nespresso coffee emits approximately 108 g CO₂-equivalent on the European market. The largest contributors to this carbon footprint are:
-
Use phase (41%), primarily driven by:
-
Cup production and washing: 25%
-
Coffee brewing: 8.5%
-
Machine manufacturing, distribution, and cleaning: 7.5%
-
-
Green coffee supply: 32%
-
Packaging: 13%, broken down into:
-
Primary (capsule) packaging: 10%
-
Secondary packaging (sleeves and cartons): 3%
-
-
Distribution: 5%
-
Overheads and support services: 5%
-
Manufacturing: 3%
-
End-of-life (recycling, incineration, or landfill of packaging and capsules): ~0% (neither significant impact nor benefit)
The cup-related impacts (production, washing, and end-of-life) -though beyond the control of the coffee provider and consistent across systems, are included in the total lifecycle as they are essential for consumption. These contribute 27 g CO₂-eq, or 25% of the total footprint.
To simplify the product’s impact for consumers, Nespresso also provides a view excluding the cup impacts. In this adjusted scenario, the contributions shift as follows:
-
Green coffee: 43%
-
Machine use: 22%
-
Capsule production: 13%
-
Distribution: 7%
-
Overheads: 7%
-
Other packaging: 3%
-
Manufacturing: 3%
-
End-of-life: 0.3%
Carbon Footprint: The carbon footprint is a measure of the potential impact on climate change. It takes into account the capacity of a greenhouse gas to influence radiative forces, expressed in terms of a reference substance and specified time horizon (100 years). The impact metric is expressed in kg CO2-eq.
End of life: The end-of-life stage includes the collection and treatment of the different packaging items, the coffee grounds, the machine and the cup.
LCA: Life Cycle Assessment
EFICO – Harvesting Coffee and Carbon
EFICO – EFICO plants trees with impact in Tanzania
CUPRIMA – Recents Developments in coffee processing – unlocking flavours
EFICO FOUNDATION – Kilimanjaro Water and Food for All – Project
EFICO FOUNDATION 20Y Flagship Project ‘Kilimanjaro Water & Food for All’
EFICO – Nicaragua SHG Rainforest Alliance Forest Positive Coffee
EFICO – Insights and Takeaways from Efico’s Sustainability Team for EUDR Compliance
EFICO – Communication of Progress Y 2024
CDP – Brewing a Sustainable Future: the Carbon Footprint of your Coffee
ScienceDirect – Comparing carbon agronomic footprint and sequestration in Central American coffee agroforestry systems and assessing trade-offs with economic returns
Barista Hustle – The Decision Tree – The Carbon Footprint of Coffee Cultivation
Espresso Outlet – Eco-friendly Wastewater Treatment Solutions for Coffee Processing Facilities
CIRAD Agricultural Research for Development – Review on Green Coffee Carbon Footprint
USAID – Scaling up Sustainable Robusta Coffee Production in Vietnam – Reducing carbon footprints while improving farm profitability
Nespresso – The Positive Cup – 2022 Progress Report